Exploring the suitable application scenarios for CDN
In an era where the internet world is becoming increasingly advanced, various internet applications are emerging. Mobile apps, static and dynamic websites, e-commerce platforms, games, live streaming, and other applications have made life more convenient. However, along with this convenience, users are also pursuing faster and more timely internet application experiences. Many users may have experienced slow website loading speeds. If a website takes longer than 3 seconds to load, users often close it and try accessing another site. Some users even joke about tapping their computers or Wi-Fi routers to make them faster (although this is proven to be futile).
This illustrates the importance users place on internet connection quality and speed.
In this fiercely competitive internet age, "internet speed" has become a battleground, leading to significant investment from many companies in research. Among these, CDN is the most widely researched and deeply applied network acceleration service. The following content will focus on the application scenarios of CDN services, hoping to shed light on its application.
What is CDN?
First, let's briefly introduce the concept and principles of CDN. CDN stands for "Content Delivery Network." Its main operating principle is to allow users to access cached content stored on the nearest nodes. This reduces the physical distance that request packets need to travel, enabling content to be delivered to users more promptly.
Please refer to the diagram:
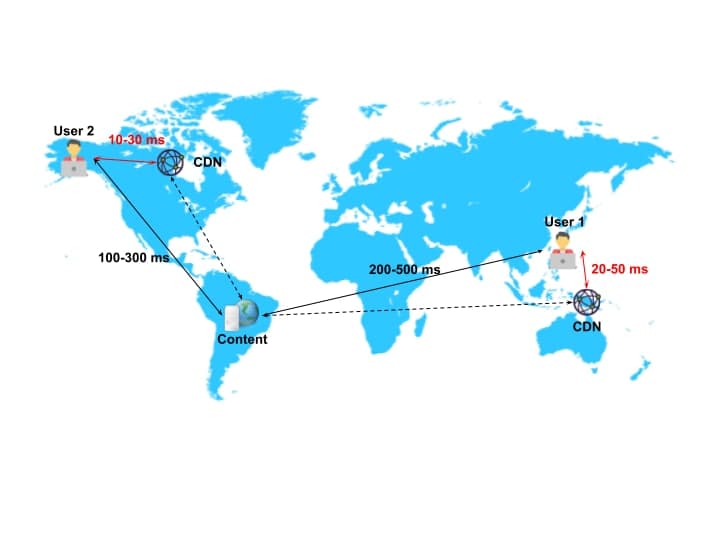
(Source:Ted Wu)
In the diagram, when a user wants to access certain content, the most common network routing involves DNS resolving the IP and accessing the remote server across continents. However, this approach often results in high latency, especially during high traffic periods or DDoS attacks, which can overwhelm the servers storing the content, leading to more serious consequences.
Through CDN technology, users can obtain data in a shorter time (as indicated in the diagram), and they can access nearby nodes through DNS and Anycast IP technology based on their location. In some cases, CDN can also mitigate the effects of DDoS attacks.
Suitable Application Scenarios for CDN
Website Acceleration: Generally, CDN is most commonly used for caching static content, such as images, website graphics, text files, video, and audio files that do not change over time. Entertainment websites, news portals, e-commerce platforms, blogs, games, and other websites are highly suitable for using CDN to cache content, speeding up page loading times, and enabling users to quickly access content.
See the diagram below:
(Source: Ted Wu)
Dynamic actions on dynamic websites such as API interfaces and database operations cannot be accelerated by traditional CDN methods. Instead, Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud offer specialized solutions for dynamic content called Dynamic CDN. The principle of Dynamic CDN involves routing optimization for user requests and accelerating the process of accessing content from the user's end to the origin server.
File Downloads: In the current internet era, the most common data, video, and audio downloads can be accelerated through CDN. For example, game update packages, map objects, audiovisual content, and text files can all be accelerated using CDN, resulting in faster delivery to the client and enhancing the user experience.
See the diagram below:
(Source:Ted Wu)
Live Streaming Applications - VOD, Live Streaming: CDN acceleration is also applicable in live streaming scenarios. As mentioned earlier, static content CDN acceleration can be used for non-time-sensitive content such as VOD and Podcast audio. This allows users to access content faster. In scenarios requiring real-time live streaming, Dynamic CDN (DCDN) is used for acceleration.
The principle of Dynamic CDN involves routing optimization by the CDN provider, enabling user requests to quickly reach the origin server for data and media file access. In China, static and dynamic CDN services are specifically distinguished. AWS offers Elemental-related services and integrates with CloudFront for acceleration. CDN applications generally fall into the three scenarios mentioned above. Different CDN providers may yield varying results based on node density and network quality in different regions. Users are advised to compare different providers before using CDN services. If assistance is needed, feel free to contact Haier Cloud via email or phone.
Solution Architecture
吳祐德 Ted Wu

