With the advance of the Internet and faster technology development, we only need physical equipment, and virtual transit could connect the world by sending email, messenger, file, and browsing websites. There are various internet protocols to regulate activities on the Internet. However, hackers will target the loophole to make malicious injections. This article aims to introduce distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS), a common cyber-attack.
What is DDoS?
DDoS is an acronym for Distributed Denial of Service, a derivative attack method of DOS (Denial of Service).
Principle:
Hackers transmit the specified type of packet or HTTPS/HTTP Request packet to the target host by IP Spoofing and controlling Zombie Computer/ BOT for passing protocols in Layer3 (network layer) and Layer4 (transmission)and Layer7 (application layer) in the OSI model. It exhausts the target host network resources (bandwidth) and system resources (CPU, RAM), making users unable to connect servers.
As an illustration:
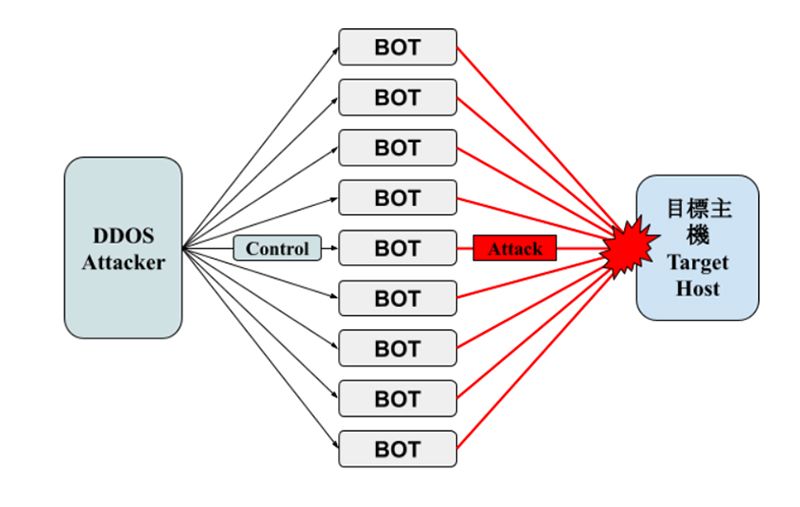
What is IP Spoofing ?
IP Spoofing modifies the source IP address within the packet based on the Internet Protocol to attack the user's IP address. Most routers forward the packet only to check the destination IP address but not identify whether the IP header is the same as the source IP in the packet, which is a typical attack on the Internet.
As an illustration:
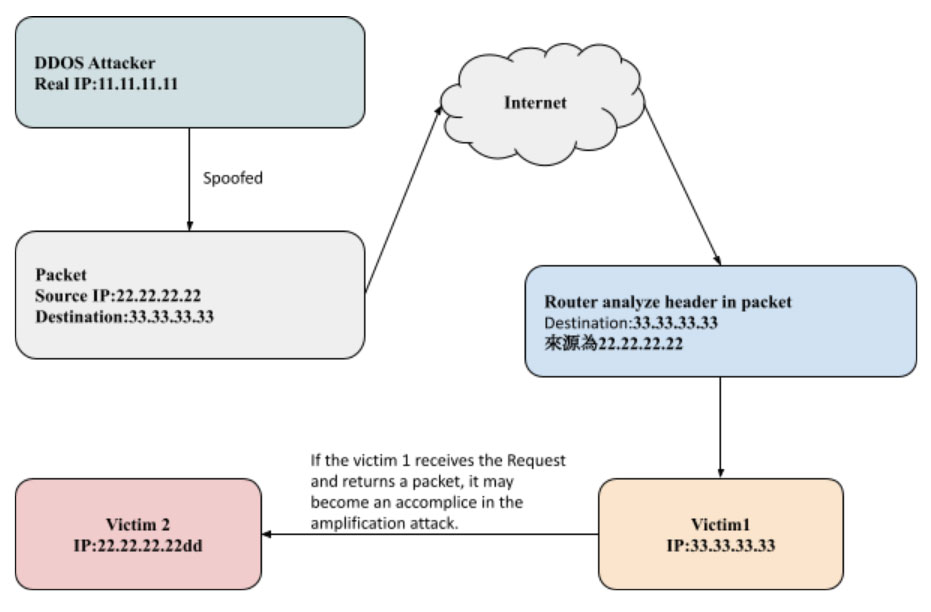
How to prevent IP Spoofing?
You can set up a firewall or gateway to do Packet Filtering for defending IP Spoofing, which will reject suspicious transmission when the source IP in the packet does not match the real IP address.
Two filtering patterns: one is from the external network to the internal network. The other is from the internal network to the external network.
Note: This prevention model cannot mitigate attacks from real IP (BOT).
- Ingress and Egress Filtering [RFC2267]
How to identify DDoS attacks?
- Suspicious connection requests from a single IP or a specific IP network segment.
- Showing a large number of unfamiliar requests in the record of the endpoint device.
- Having connection requests with the same connection characteristics, such as a single region and a single time.
- CPU and RAM usage has increased sharply.
- The service is suddenly interrupted, or the service access speed drops sharply.
All of the above situations show that DDoS attacks may happen. Therefore, you had better check the records on the device side and confirm the website traffic and CPU usage by examining MRTG (Multi Router Traffic Grapher), a monitoring software. If you have not installed it, please contact your ISP.
Types of DDoS attacks (classified based on the OSI 7 Layer Model for Network Protocol)
The types of DDoS attacks are diverse, so let’s see the most common attack methods in the following paragraph.
Layer3 – including IP Spoofing、IPSec、ICMP Attack、ARP Spoofing
a.ICMP[1] Flooding Attack:
Definition:
The most common is the DOS-Ping flood attack. That is, a BOT sends numerous Ping requests. On the other hand, if many BOTs send Ping requests, it is called DDoS Ping attacks.
Solution:
Many public cloud providers have the Anycast IP Load Balance service, which distributes ICMP requests by transiting many cloud providers' global nodes. Also, you can stop the ICMP from protecting servers by using this service.
Layer4 - TCP
a.SYN Flood
Definition:
Under normal circumstances, the attack is carried out through the TCP three-way handshake protocol [2].
Step 1: Server A will send an SYN packet to establish the first connection.
Step 2: After Server B receiving the packet, Server B sends back an SYN/ACK packet to confirm.
Step 3: Server A sends back an ACK packet to confirm the establishment of the connection.
SYN flood attack uses multiple BOTs sending the SYN in the first step. The target server then sends back the SYN/ACK packet. However, BOTs intentionally do not return the ACK package response, which causes the target server to open a temporary port to maintain the session for receiving. It aims to exhaust the target server.
As an illustration:
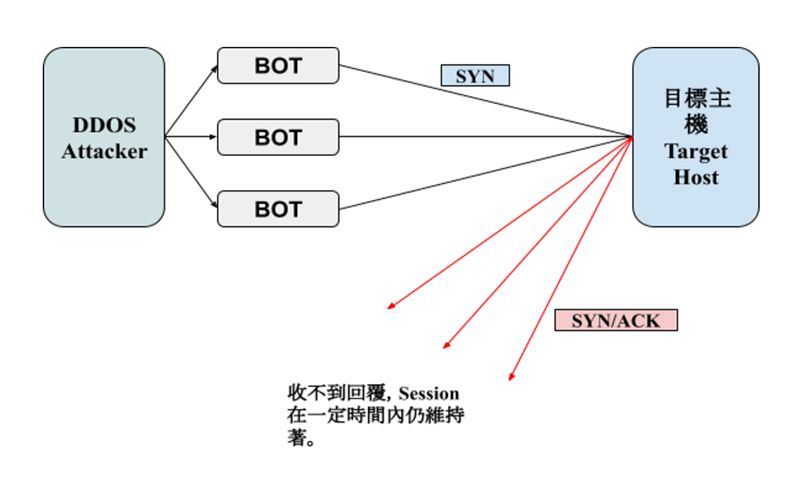
Solution:
- Use Anti-DDoS or such cloud tools to lead malicious traffic into the cleaning center or blackhole filtering for cleaning.
- Establish a Proxy Server, usually a firewall, to replace the original server for establishing an external connection. After establishing a successful connection, the traffic will be imported into the original server.
- Modify the settings in the machine. When the latest TCP connection comes in, it will cover the temporary port that has not yet established a connection.
b.ACK Flood
Definition:
The client-side will send an ACK packet to the host server, which confirms data have been successfully transmitted and data sequences are correct.
On the other hand, the host server would check the ACK packet for the packet’s status and content, which continuously consumes the host server's computing resources. If the package shows that the data is not successfully transmitted, the host server will send data again.
Therefore, hackers can paralyze the host server with many malicious ACK packet after establishing a TCP connection so that actual ACK packets cannot be responded to.
Solution:
Connect with the client-side through Anycast IP Proxy, and also use cloud tools to determine whether the IP source is suspicious and do attack detection simultaneously. If it detects attacked behaviors, it automatically directs traffic into the cleaning center for near-source cleaning.
Layer4 - UDP
a.UDP Flood
Definition:
UDP flood attack is a common UDP DDoS attack method.
Since the UDP protocol is a non-connection protocol, the attacker sends many UDP packets with random port numbers and spoofing IPs to the host server.
The host receiving the UDP packet will consume resources to check whether a program receives packets on this port number. If no program receives packets on this port, it will send ICMP (Ping) to the sender. Therefore, the attacker uses many bots to send UDP packets, which causes bandwidth load and exhausts the host server.
Solution:
Anycast IP, a service in cloud platforms, can lead the traffic away from the host side. And also, targeting numerous repeated UDP packets, each cloud node will take the first protection measures to ensure the security of the host side.
b.DNS Amplification Attack
Definition:
The principle of the amplification attack is to send a small request. After these requests pass on, the response packet become larger than the original request packet. Then, all response packets are sent to users by IP Spoofing.
DNS amplification attack means that the attacker pretends to be a normal server, initiates a DNS query, and then replaces the IP address from the packet to the victim’s IP address. It will cause the victim’s server to be stuffed into large packets, causing the service unable to work.
Solution:
- Increase bandwidth.
- Use DDoS protection products to clean up suspicious traffic.
- Set up the firewall to check the source IP of the packet. If IP address is suspicious, refuse to accept it.
c.NTP Amplification Attack
Definition:
The principle of the amplification attack is to send a small request. After these requests pass on, the response packet is large than the original request packet. Then, all response packets are sent to users by IP Spoofing.
The NTP amplification attack bases on the NTP (Network Time Protocol) protocol. Since NTP is also a UDP protocol, it does not include a check process. The principle of the NTP attack is through a command called Monlist, which is mainly used to check the NTP server connection status and return the IPs of the last 600 hosts that have been time synchronized with the NTP server.
Therefore, the NTP amplification attack includes that IP Spoofing is used to counterfeit IPs and send Monlist commands, making the returned packets back to the victim host server.
Solution:
- Update NTP Server to the latest version to avoid being used by malicious people.
- Firewall ACL (ACL = Access Control List)
- DDoS is diverted to the cleaning center for website traffic cleaning.
Conclusion
The above is only a basic DDoS introduction and what attack types have mentioned are merely the tip of the iceberg. Nowadays, DDoS attacks frequently happen on the Internet.We should pay attention to how to prevent service without interruption when encountering an attack so that avoid business losses
Higher Cloud
HigherCloud provides multi-cloud services and also specializes in networks and infrastructure design.
According to versatile DDoS attacks, we have different architecture plans for customers. Also, HigherCloud has many cases in successfully helping clients in resisting DDoS attacks. We love hearing from you. Feel free to contact us!

