The impact of the 2020 pandemic on global industries began to unfold, leading governments and various sectors to adopt various work patterns to maintain normal operations. Enterprises began to embrace the work-from-home (WFH) model, with Twitter announcing permanent remote work, and Facebook aiming to transition half of its employees to remote work over the next 5 years.
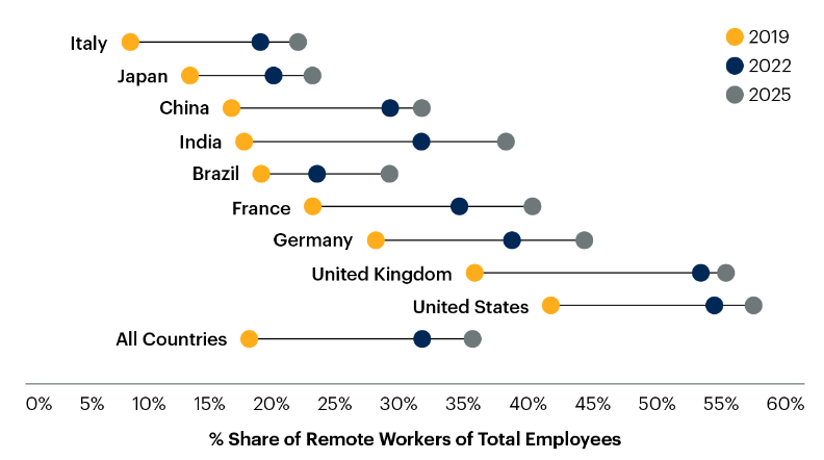
According to 2022 Gartner analysis, there are already 31% of remote workers globally. With the widespread vaccination and people's familiarity with the WFH model from 2020 to 2023, a significant shift in work patterns is rapidly brewing. With the rapid development of information technology, some companies are questioning the necessity of centralized office work. Even when separated, employees are performing well. Consequently, more and more enterprises are exploring the work-from-anywhere (WFA) model that emerged in the post-pandemic era. Employees no longer need to worry about commuting time, companies save office costs, and it becomes easier to hire talent globally without concerns about immigration issues.
全球遠端工作趨勢(引用:Gartner Hybrid and Remote Workers Change How They Use IT Equipment)
Remote connectivity in enterprises faces risks related to information system security over long distances.
The significant lifestyle changes caused by the pandemic have led to a substantial increase in remote work patterns, which in turn has heightened related cybersecurity threats. Common remote connection technologies include VPN, SSH, and RDP, which allow users to access and control remote computer services anytime, anywhere.
One of the major challenges faced by remote-working enterprises is conducting meetings and accessing internal company systems and documents. For the former, there are many readily available SaaS (Software as a Service) solutions in the market, such as Google Meet, Teams, Zoom, etc., offering secure and comprehensive remote meeting capabilities. As for accessing internal company services, employees traditionally connect remotely to the company via the internet, using remote connection protocols such as RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) and SSH (Secure Shell). Commercial software solutions like TeamViewer, Splashtop, Netop, Chrome Remote Desktop, and Windows Remote Desktop Connection provide short-term solutions to remote connectivity issues.
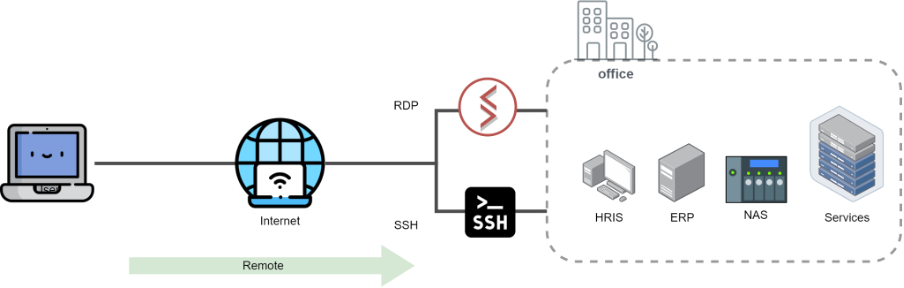
Security vulnerabilities in RDP and SSH: While remote protocols like RDP and SSH offer convenient remote operations, the widespread adoption of remote work patterns has also brought about certain security vulnerabilities:
- RDP does not encrypt transmissions by default, making RDP connections over the Internet susceptible to interception.
- Both RDP and SSH default to username and password authentication, posing a risk of compromise if account information is leaked.
- RDP has multiple known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit to gain access to systems, such as BlueKeep, DejaBlue, CVE-2019-9510, etc.
- SSH also has vulnerabilities like CVE-2019-6111, affecting PuTTY connection tools by allowing injection of malicious code during SSH connections, bypassing authentication for unauthorized access to target systems.
Common enterprise security connection protections: Using VPN as a secure gateway to access the enterprise network environment. Internal enterprise services are established within a closed network environment, and all external connections must pass through VPN-controlled user account login and encrypt data packets for transmission, significantly enhancing connection security.
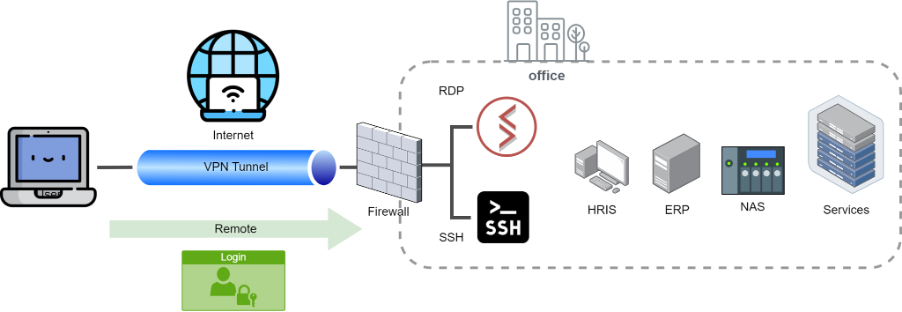
Even with enterprise connections passing through VPN, there are still security risks. While encrypting transmissions and closing off external connections to enterprise internal services through VPN can significantly enhance connection security, the growing reliance on remote operations has led to the emergence of various attack methods:
- Weak passwords used by VPN users may easily allow hackers to gain entry into the enterprise environment, posing a risk.
- End-user terminal environments that have been infected with viruses or trojans can indirectly impact the enterprise environment.
- Vulnerabilities in encryption protocols on VPN servers, such as Heartbleed, can lead to data theft by hackers affecting VPN servers that have been compromised.
While enterprises significantly reduce cybersecurity risks through VPN, there are indeed risks that need to be addressed, including implementing robust end-user information security education, strict security measures such as enhanced authentication, strong passwords, and rigorous access controls. Experienced personnel are needed to ensure the security of enterprise connections.
This article mainly analyzes the current situation, and the next issue will continue to explore the challenges of next-generation remote connections and the solutions they bring forth!
CTO
藍國豪 Levi Lan